Are you new to WordPress and wondering about the different user roles? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the world of WordPress user roles and their significance. Whether you want to manage a blog, collaborate with a team, or simply control the access levels on your website, understanding WordPress user roles is essential. From administrators with full control to contributors with limited access, we will unravel the possibilities and empower you to effectively manage your WordPress site. So, let’s dive in and get familiar with WordPress user roles!
Table of Contents
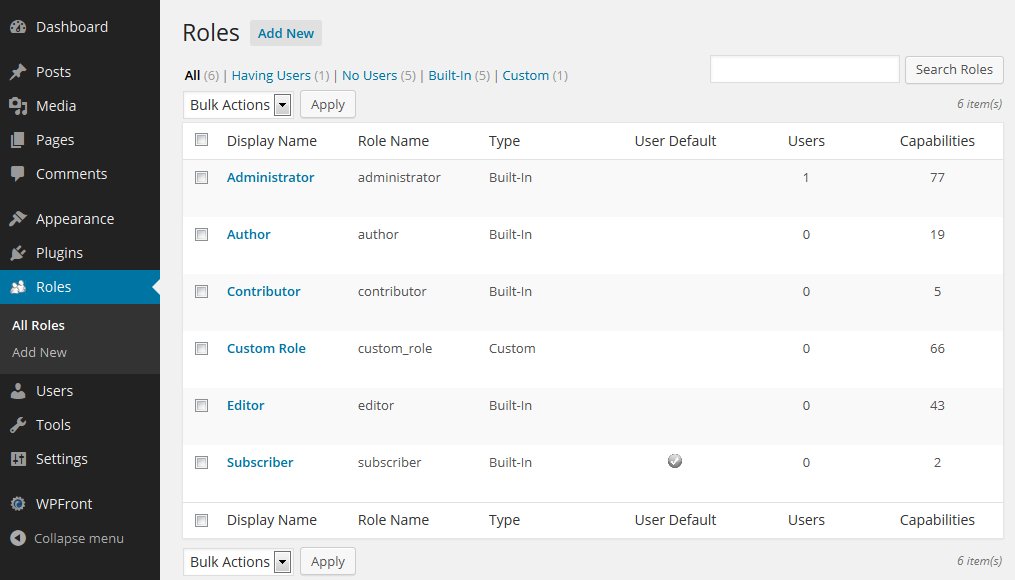
WordPress User Roles: A Comprehensive Guide
WordPress, one of the most popular content management systems (CMS) in the world, offers a wide range of capabilities to create and manage websites. One of its key features is the ability to assign different user roles, each with its own set of permissions and capabilities. Understanding WordPress user roles is crucial for effectively managing your website and controlling user access. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different user roles in WordPress and their specific responsibilities and capabilities.
1. Administrator
The Administrator role is the highest level of access in WordPress, granting complete control over the website. Users with this role have the authority to perform all tasks within WordPress, including managing plugins, themes, user accounts, and site settings. Administrators can add, edit, or delete content, create new user accounts, and change website settings. They have the power to install, activate, or deactivate plugins and themes, and can even modify the website’s core files.
Key Responsibilities and Capabilities of Administrators:
- Manage all aspects of the website, including content, plugins, themes, and settings.
- Create, edit, and delete user accounts, assign user roles, and modify user information.
- Install and configure plugins and themes.
- Customize the appearance and functionality of the website.
- Manage website security and perform regular backups.
- Access and modify the website’s core files.
2. Editor
The Editor role is primarily focused on content management. Users with the Editor role can create, edit, publish, and delete any posts or pages on the website. They have complete control over the content, ensuring its quality, accuracy, and consistency. Editors can moderate comments, manage categories and tags, and even assign articles to other authors or contributors.
Key Responsibilities and Capabilities of Editors:
- Create, edit, publish, and delete posts and pages.
- Manage and moderate comments.
- Assign articles to other authors or contributors.
- Manage categories and tags.
- Review and revise content for quality and accuracy.
3. Author
The Author role is designed for individuals who contribute original content to the website. Users with the Author role can create, edit, and publish their own posts, but do not have the ability to modify or publish posts created by other users. Authors can manage their own media files and can moderate comments on their own posts.
Key Responsibilities and Capabilities of Authors:
- Create, edit, and publish their own posts.
- Manage their own media files.
- Moderate comments on their own posts.
- Cannot publish or modify posts created by other users.
4. Contributor
The Contributor role is ideal for individuals who want to contribute content to the website but do not require full publishing capabilities. Users with the Contributor role can create and edit their own posts, but they cannot publish them directly. Instead, their posts need to be reviewed and approved by an Editor or Administrator before they can be published. Contributors cannot modify or delete posts created by other users.
Key Responsibilities and Capabilities of Contributors:
- Create and edit their own posts.
- Submit posts for review and approval.
- Cannot publish or modify posts created by other users.
5. Subscriber
The Subscriber role is the most limited user role in WordPress. Users with the Subscriber role can only manage their own user profile and view content that is publicly available. Subscribers cannot create, edit, or publish any posts, nor can they modify any settings or install plugins and themes.
Key Responsibilities and Capabilities of Subscribers:
- Manage their own user profile.
- View publicly available content.
- Cannot create, edit, or publish posts.
- Cannot modify settings or install plugins and themes.
6. Custom User Roles
WordPress also allows administrators to create custom user roles to meet specific website needs. This flexibility enables administrators to tailor user roles and permissions based on their unique requirements. By creating custom user roles, administrators can grant specific capabilities to users and control their access to various aspects of the website.
Key Benefits of Custom User Roles:
- Fine-tune user access and permissions.
- Create specialized roles for specific tasks or responsibilities.
- Enhance website security by limiting user access to sensitive areas.
- Streamline workflows by assigning roles with specific capabilities.
7. Best Practices for Managing User Roles in WordPress
When managing user roles in WordPress, it is important to follow best practices to ensure the security and integrity of your website. Here are some key tips to consider:
- Assign user roles based on the specific responsibilities and needs of each user.
- Regularly review and update user roles as the website evolves and user responsibilities change.
- Limit the number of Administrators to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and modifications.
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication for administrative accounts.
- Regularly backup your website to protect against data loss or accidental changes.
- Ensure that users have only the necessary capabilities for their roles to prevent unauthorized actions.
By following these best practices, you can effectively manage user roles and permissions in WordPress and maintain the security and functionality of your website.
WordPress User Roles and Permission Management Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
What are WordPress user roles?
WordPress user roles define the level of access and capabilities that different users have within a WordPress website. Each role has its own set of permissions, allowing users to perform specific tasks and access certain areas of the website.
What are the default WordPress user roles?
The default WordPress user roles are Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber. Each role has different capabilities and responsibilities. The Administrator has full control over the website, while the Subscriber has the least amount of access.
Can I create custom user roles in WordPress?
Yes, you can create custom user roles in WordPress. Although the default roles cover most common needs, there are cases where you might want to create a role with specific capabilities tailored to your website’s requirements. You can use plugins or custom code to create and assign custom user roles.
What capabilities does the Administrator role have?
The Administrator role in WordPress has the highest level of access. Administrators can manage all aspects of the website, including creating and deleting users, installing plugins and themes, editing code, and modifying site settings. It is recommended to limit the number of users with Administrator roles to ensure better security.
What is the difference between Author and Contributor roles?
The Author role in WordPress can create, edit, publish, and delete their own posts, as well as upload media files. They have more control over their content compared to Contributors. On the other hand, Contributors can write and edit their own posts, but they cannot publish them. They need an Editor or Administrator to review and publish their content.
What can Subscribers do in WordPress?
Subscribers have the most limited role in WordPress. They can only modify their own user profile, leave comments on the website, and receive email notifications for new posts. Subscribers cannot create or edit any content on the website.
Final Thoughts
WordPress user roles play a crucial role in managing the access levels and responsibilities of individuals within a WordPress website. By assigning different user roles such as administrator, editor, author, contributor, and subscriber, website owners can ensure that each user has the appropriate privileges and limitations. Administrators have full control, editors can manage content, authors can publish their own posts, contributors can write but not publish content, and subscribers have limited access for commenting and updating their profiles. Understanding and utilizing WordPress user roles effectively can help maintain security, streamline workflows, and enhance collaboration within a WordPress-powered website. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced WordPress user, mastering the concept of user roles is essential.